October 2025
A | B | C | D |E | G | H | I | L | M | N | O | P | R | S | U | W
Glossary
A
Allocation
The maximum volume of nonsaline water licensed for use under the Water Act. Allocation may also refer to a water diversion volume, rate, and timing.
Alternative water (other)
Water other than alternative nonsaline water (see definition below) is considered “other alternatives” to nonsaline water. Examples of other water include
- saline groundwater,
- produced water from oil and gas wells linked to an external project,
- hydraulic fracturing flowback water from a well or wells linked to an external project, and
- wastewater (i.e., landfill leachate and water sent to disposal wells).
Alternative nonsaline water
Includes nonsaline surface water and nonsaline groundwater that is highly mineralized (but meets the definition of nonsaline water) due to the geological setting or was used and adversely affected by industrial, commercial, or municipal activities.
Alternative nonsaline: groundwater
Alternative nonsaline groundwater has a total dissolved solids content of 4000 milligrams per litre (mg/L) or less. It includes relatively deep groundwater that does not directly support instream flow. The figure below shows how to determine whether nonsaline groundwater is considered “alternative” or “high quality.”
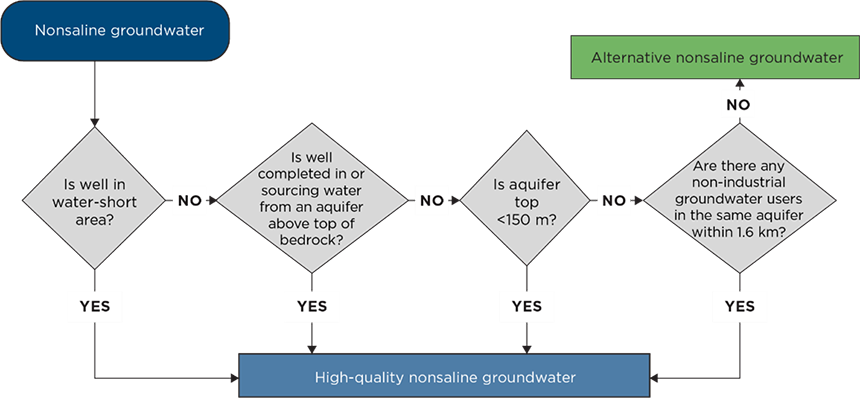
Sources of alternative nonsaline groundwater also include the following:
- nonsaline groundwater in contact with bitumen deposits, regardless of depth
- nonsaline groundwater that naturally contains hydrocarbons (excluding methane) in formations that contain water and hydrocarbon resources, regardless of depth
- contaminated nonsaline groundwater sourced from remediation wells
Alternative nonsaline: surface water
Sources of alternative nonsaline surface water include the following:
- industrial runoff from areas that are not water short
- municipal or industrial wastewater
- oil sands process-affected water (tailings water) from an oil sands mine
- runoff in contact with bitumen or saline groundwater from an oil sands mine
- captured/condensed steam from flue gas heat recovery systems
Apportionment
When waters of transboundary watercourses are shared, Alberta permits a quantity of water equal to a portion of the natural flow of each watercourse to flow into other provinces or jurisdictions. Apportionment is the legal allocation determining how much water each jurisdiction can use.
Apportionment agreement
Alberta has formal agreements with downstream neighbours (interprovincial and international) to allow for specific minimum volumes of water to flow into their jurisdictions.
Availability
The estimated volume of nonsaline water in Alberta each year. It is derived from estimates of surface water sources and mapped shallow nonsaline groundwater sources.
B
Barrel (bbl)
A standard measure of volume used in oilfield operations; 1 barrel is approximately 159 litres, or 42 US gallons. Approximately 6.2929 barrels are in one cubic metre of oil, while approximately 6.2901 barrels are in one cubic metre of water.
Barrel of oil equivalent (BOE)
A unit of measure that allows one to standardize production volumes from different energy resources, such as natural gas, condensate, and different types of crude oils. In this report, different types of hydrocarbons are converted to a standard barrel of light-medium crude (38.5 GJ) for the purposes of comparing water use intensity.
For example, one cubic metre of bitumen converts to 42.8 GJ (see ST98). Dividing that by 38.5, and multiplying by 6.2929 to convert cubic metres to barrels gives the BOE. Therefore, one cubic metre of bitumen is equal to approximately 7.00 BOE.
C
Conservation
Any beneficial reduction in water use, loss or waste, or practices that improve the use of water to benefit people or the environment.
Cumulative surface water availability or allocation
Map values that include contributing upstream sources in the allocated or available volumes of surface water for a hydrologic unit code 8 area. Values that do not include upstream contributions are categorized as "local."
D
Diversion
Removing nonsaline water from a lake, river, run-off collection pond, aquifer, or other water body for any purpose, including energy development.
E
Efficiency (of water use)
Efficiency is an indicator of the relationship between the amount of water required for a particular purpose and the quantity of water used or diverted.
F
Flowback
Hydraulic fracturing fluid that flows back to the wellbore after fracturing is complete.
G
Groundwater
Water in pore spaces or fractures beneath the Earth’s surface.
Groundwater availability
The average annual groundwater recharge from precipitation (rainfall or snowmelt) that percolates into the sediments above the bedrock and the bedrock within 150 metres of the surface. Groundwater availability is estimated and aggregated at the hydrologic unit code 8 scale.
H
Hydrologic unit code 8 (HUC 8)
A classification based on a system developed by the United States Geological Survey that divides an area into smaller and smaller hydrologic units and that was adapted by the Government of Alberta for use in Alberta. The province has five HUCs, from coarsest to finest level: HUC 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10.
High-quality nonsaline water
High-quality nonsaline water includes high-quality nonsaline groundwater and high-quality surface water that support instream flow or are usable with standard treatment technologies for drinking water supplies and livestock watering.
High-quality nonsaline: groundwater
Groundwater with a total dissolved solids content of 4000 mg/L or less. Sources of high-quality nonsaline groundwater include
- shallow aquifers, where the top of the aquifer is less than 150 m from the surface,
- aquifers in sediments above the top of bedrock, regardless of depth,
- aquifers in water-short areas, regardless of depth, and
- aquifers with nonindustrial water users accessing the same aquifer within 1.6 km of the diversion, regardless of depth.
High-quality nonsaline: surface water
Surface water sourced from streams, rivers, lakes, springs, wetlands, and from manmade water bodies, such as:
- canals and ditches
- dugouts
- reservoirs
- borrow pits
- raw water ponds
- nonindustrial runoff (stormwater) ponds
- industrial runoff ponds in water-short areas
- reclaimed water bodies and end-pit lakes
- gravel pits
- quarries
I
Instream flow needs
The acceptable flow rate and volume of water (instream flow) required to sustain a natural watercourse. The instream flow considers the ecological function of a watercourse (e.g., protection of fish habitat, migration, and propagation; wildlife habitat; water quality; and ecosystem maintenance) and human needs such as recreation, navigation, and hydropower generation.
In situ (oil sands thermal)
A process where steam is injected into heavy oil / bitumen deposits to reduce viscosity.
L
Local surface water availability or allocation
Map values of the surface water volumes allocated or available for a hydrologic unit code 8 area, excluding contributions from upstream sources. Values that include upstream contributions are categorized as "cumulative."
M
Make-up water
Water added to an energy process to replenish water lost during that process. Make-up water supplements recycled water and can be obtained from nonsaline or alternative water sources. Produced water transferred from one scheme to another for reuse is reported as alternative make-up water.
N
Nonsaline water
Water having a total dissolved solids content of 4000 milligrams per litre or less. Sometimes referred to as fresh water, but it may require treatment before domestic or agricultural use.
Nonsaline water-use intensity
The volume of nonsaline water (in barrels) that is used to produce one barrel of oil equivalent.
P
Polymers
Fluids that are added to injection water to increase the viscosity of the water and improve recovery.
Process-affected water
Alternative nonsaline make-up water received from the wastewater stream of an oil sands mine.
Produced water
Water naturally present in the reservoir that is produced in association with hydrocarbons from a well licensed for hydrocarbon production. For in situ and enhanced oil recovery projects, produced water is initially pure formation water but transitions to a mixture of water having a high composition of injected water (i.e., in the form of steam or recycled water mixed with make-up water). Produced water use reported may include wastewater injected into disposal wells.
Proppant
Proppants are used in hydraulic fracturing to keep fractures open. Sand or ceramic materials are typical.
R
Recycled water
Water previously used in or produced from an energy activity then reused by operators in that same process. It does not include water transfers from external projects.
S
Saline groundwater
Groundwater with a concentration of total dissolved solids greater than 4000 milligrams per litre.
Surface water
Water on the ground surface, including water in lakes, rivers, and run-off collection ponds, natural or manmade.
Surface water availability
Surface water availability data comes from Agriculture Agri-Food Canada Annual Unit Runoff in Canada – 2013. Although the unit runoff data set is from 2013, the median runoff values remain relatively stable.
Surfactants
Fluids that are added to injection water to reduce the tension between oil and water; the less tension between the materials, the more easily oil can be recovered.
U
Use
The actual volume of water used by an operator.
W
Watershed
An area of land that catches precipitation (rain, snow) that drains or seeps into a common stream, lake, or river. The boundaries of a watershed are topographically high points on the land.


